Difference between revisions of "Energy Storage 101/Drivers and Big Picture"
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
=Current Status and Future Outlook= | =Current Status and Future Outlook= | ||
==Energy Storage Deployment Trends== | ==Energy Storage Deployment Trends== | ||
<!--[[File:Deployment_Breakdown.PNG|none|thumb|800px|Who is deploying storage and where? Source: [https://www.eia.gov/electricity/data/eia860/ US Energy Information Administration Form EIA-860]]]--> | |||
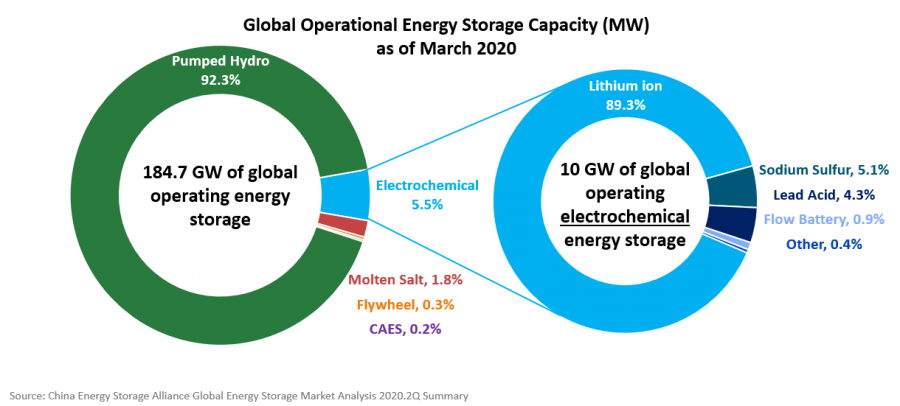
==Deployments by Technology== | ==Deployments by Technology== | ||
Revision as of 09:53, 9 November 2020
Drivers for Energy Storage
Decreases in Technology Costs
Massive research and development investment and manufacturing scale-up has driven costs down for lithium ion battery storage. This was initially driven by the consumer electronics market (e.g. cell phones and laptops) and more recently accelerated by the electric vehicle market. There has been an almost 90% reduction in $/kWh cost in the last decade and lithium ion costs are expected to continue to decrease with additional manufacturing improvements and economies of scale. Solar and wind technology cost reductions are also driving deployment of energy storage for hybrid applications. Bloomberg New Energy Finance projects 2030 lithium ion pack costs at $62/kWh based on observed prices and an 18% learning rate. Source: BNEF: "A Behind the Scenes Take on Lithium-ion Battery Prices"
Increasing Renewable Generation
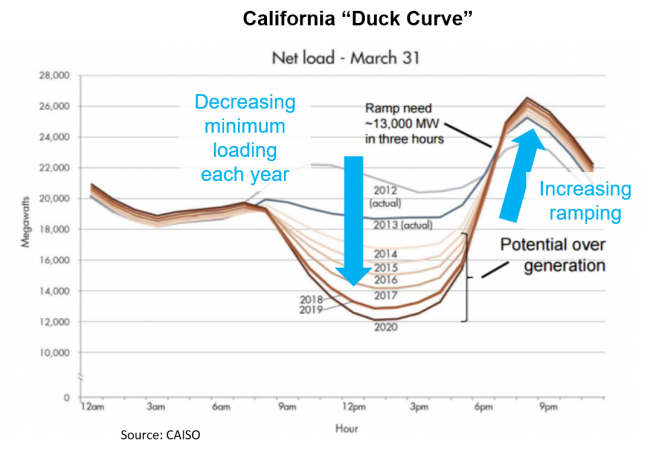
Solar photovoltaic (PV) is driving midday over generation and increased evening ramping requirements which provides a value stream for flexible energy storage. As more solar comes online, the effective net load in the middle of the day decreases. Wind energy is similarly driving flexibility needs.
Evolving Utility Needs
- The grid infrastructure (generation, transmission, and distribution) is sized for infrequent peak needs and therefore most assets are under-utilized most of the time. Energy storage can support peak load reduction to provide significant cost reduction opportunity to electricity customers.
- Utility asset infrastructure is aging and peak load reduction may extend asset life and offer opportunity to consider investment in new technologies.
- Peaker plants are only used a fraction of hours per year and energy storage is being considered as peaking capacity in generation planning. Battery storage is already being deployed for this application and as costs decrease they may be cost competitive with combustion turbines in the next decade. When accounting for operational benefits, the crossover point on cost may be sooner.
Increasing Utility Customer Choice and Engagement
Customers (residential, commercial, industrial) are considering energy storage for:
- Bill savings
- Increased energy independence
- Renewable energy goals
- Backup premise or critical loads
Policy and Regulatory Changes
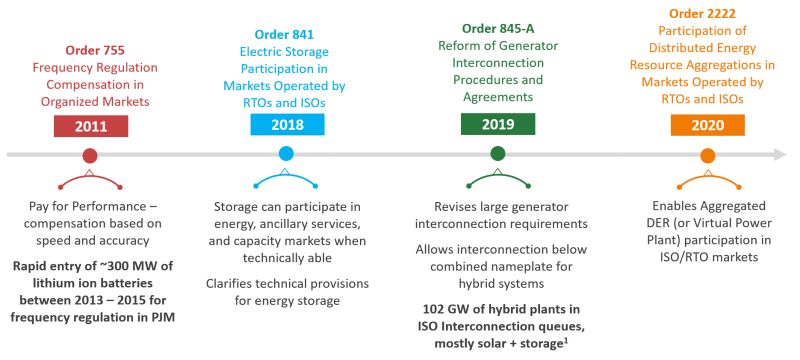
U.S. Federal Policy
In the last decade there has been a shift in policy towards energy storage. At the federal level, FERC has issued several orders as outline below to support energy storage in markets.
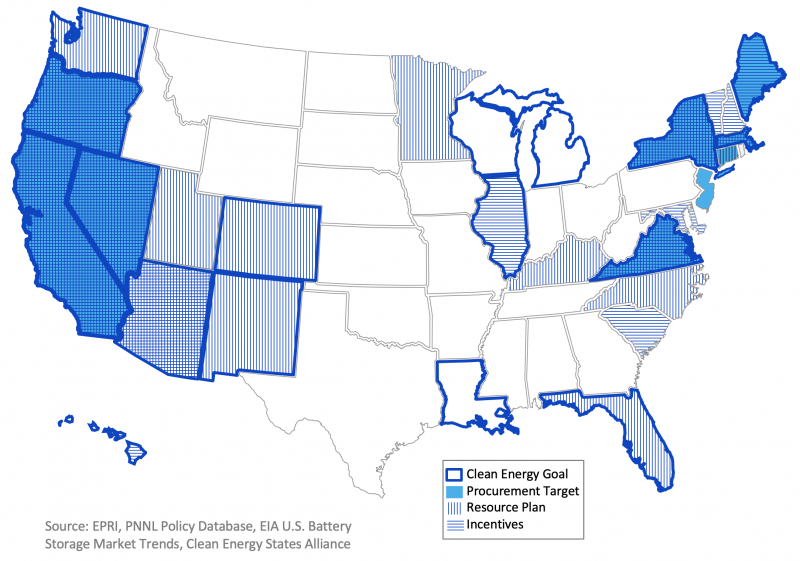
U.S. State Policy
At the state level, there has been an expanding number of policies to address energy storage in various ways.
Procurement Targets: Regulators or legislators set procurement goals and mandates requiring utilities to directly procure or contract storage.
Incentives: Legislators create economic incentives (e.g. rebates or subsidies) for deploying storage; No mandatory procurement
Resource Plans: State agencies or regulators fund studies or direct utilities to create an energy plan with consideration of storage; No targets or incentive
Current Status and Future Outlook
Energy Storage Deployment Trends
Deployments by Technology