Basic Technology Characteristics
|
| How it Works:
|
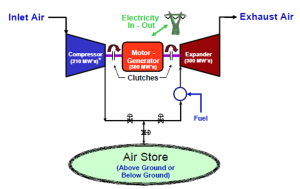
Air is compressed (charging), stored, and expanded (discharging).
|
| Benefits:
|
- Mature bulk storage
- Low cost per kWh potential
|
| Challenges:
|
- Geographical limitations
- Requires fuel for heating producing CO2 emissions
|
| Technology Variations:
|
|
| Applications:
|
Bulk, long-duration services
|
| AC RTE Efficiency:
|
40-55%
|
| Cycle Life:
|
30 years
|
| Technology Readiness Level (TRL):
|
9 - Fully Mature
|
| Installed Capacity:
|
~500 MW
|