Basic Technology Characteristics
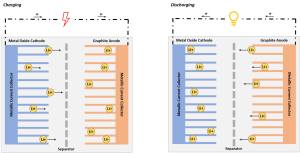
An image showing the general chemical structure of a lithium ion cell
|
| How it Works:
|
Shuttle lithium ions (Li+) between cathode (+) and anode (-). Fully charged when Lithium ions are fully intercalated in the anode.
|
| Benefits:
|
- High power and energy density
- Low self-discharge rate
- High roundtrip efficiency
- Flexible configurations
- Leverage cost reductions from consumer electronics and electric vehicle markets
|
| Challenges:
|
- Cycle life limitations, especially with high depth of discharge
- Safety concerns around fire and explosion risk
- Supply chain constraints
|
| Technology Variations:
|
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP),
Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC),
Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA),
Lithium Titanate Oxide (LTO)
|
| Applications:
|
Diverse applications from minutes to hours duration and from small scale residential to transmission connected.
|
| AC RTE Efficiency:
|
80-92%
|
| Cycle Life:
|
3,000 - 10,000 cycles
10 - 20 years
|
| Technology Readiness Level (TRL):
|
9 - Deployed
|
| Installed Capacity:
|
>10 GW
|